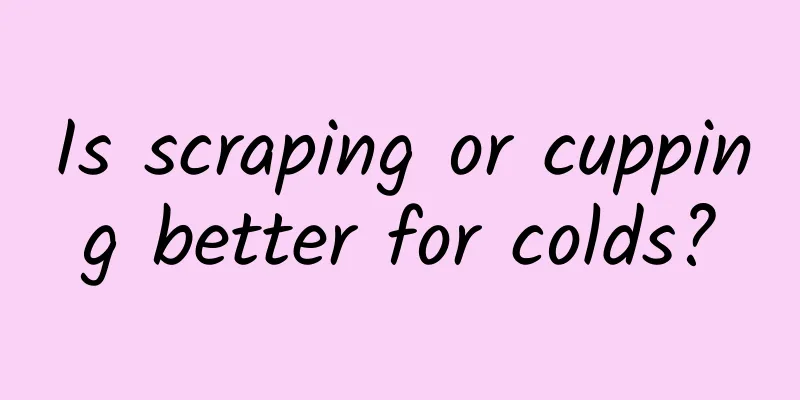Classification of corticosteroids

|
Hormone drugs are mainly used to regulate the body's water and salt metabolism and sugar metabolism. For example, after entering the blood circulation, corticosteroids can promote reactions with specific proteins in the blood, thereby regulating the concentration of free steroids in the blood. There are generally five types of corticosteroids, such as sex hormones, adrenal cortex hormones, thyroid hormones, insulin, and five anterior pituitary hormones. If classified by drug type, it can be divided into the following five categories: 1. Adrenal cortical hormones: including adrenocorticotropic hormone, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids. 2. Sex hormones: including estrogens, progestins, androgens, anabolic hormones, and gonadotropins 3. Thyroid hormones: including thyroid stimulating hormone and thyroid hormones. 4. Insulin: including long-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin and short-acting insulin. 5. Anterior pituitary hormones: including growth hormones, somatostatins, growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) and similar drugs, and adrenocorticotropic hormone-releasing hormone. Clinical Application ① Adrenal cortex insufficiency. ②Autoimmune diseases. ③Allergic diseases. ④Inhibit rejection during organ transplantation. ⑤Infectious diseases. ⑥Shock. ⑦Tumor. ⑧Liver disease. ⑨Ophthalmological and skin diseases . ⑩Myasthenia gravis. Auxiliary diagnosis of certain endocrine diseases. In short, corticosteroids are mainly used to rescue critically ill patients and treat certain chronic diseases that are not responsive to other drug treatments, such as rheumatoid arthritis and frequent asthma. Although it has definite antipyretic and analgesic effects, corticosteroids have too many serious adverse reactions. Adverse Reactions Corticosteroid hyperfunction; steroid diabetes; muscular atrophy and osteoporosis; inducing and aggravating infection; inducing and aggravating ulcers; inducing mental symptoms; concurrent eye diseases; teratogenicity; inappropriate drug withdrawal may also lead to cortical insufficiency, hormone withdrawal syndrome and symptom rebound. |
<<: What's wrong with corticosteroid face?
>>: Mnemonics for the effects of corticosteroids
Recommend
Can chronic gastritis eat glutinous rice?
Diet has always been the focus of attention for p...
Chronic infantile hypoxia
Everyone knows about hypoxia. Hypoxia means lack ...
Bone pain during early pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, bone pain occur...
What are some tips for rotting lips?
What we often call sore corners of the mouth refe...
Can early vitiligo be cured?
Vitiligo is a skin disease that concerns many peo...
The consequence of having phlegm in the throat after vaccination
The emergence of vaccines has made a great contri...
Symptoms of tuberculosis
Diseases pose a great threat to the human body. O...
What is prostate calcification?
Many men have prostate diseases. There are many t...
Are there serious side effects of Jianer Pills?
Although children's metabolism is very rapid, ...
Clinical manifestations of mild lumbar degeneration
Speaking of mild lumbar degeneration, many friend...
How to treat prostatitis
For most of our male friends, prostatitis should ...
Functions and effects of vitamin B
Vitamin B plays a very important role for the hum...
What happens if prolactin is too high?
High prolactin is a common disease nowadays, whic...
What is the success rate of brainstem hemangioma surgery?
The brain is the most important organ in the huma...
What is the best sleeping posture for lumbar spondylolisthesis? What should you pay attention to for lumbar spondylolisthesis?
In life, especially those who sit in the office f...