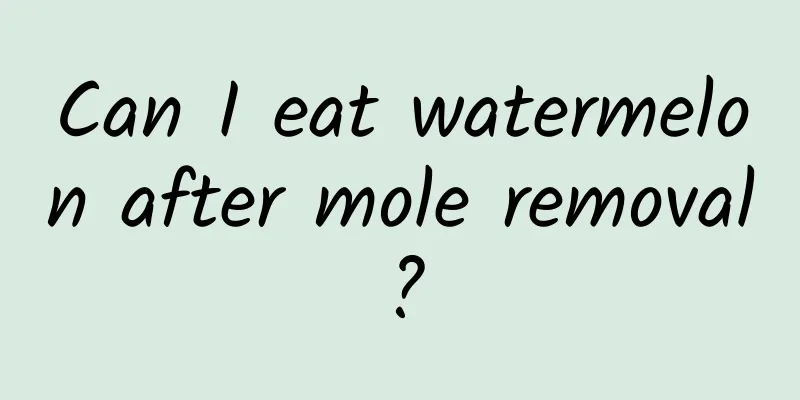Micronodules in the right lower lobe

|
During a physical examination or when people with lung discomfort are diagnosed with lung nodules, they will become particularly nervous, fearing that they have lung cancer. However, there is actually no need to worry too early. Nodules in the lungs, like nodules in other parts of the body, can be benign or malignant. Only the malignant ones may be tumors. Now that medicine is more advanced, we can determine the nature of nodules. This article introduces the relevant content about lung nodules, you can take a look. In the thoracic surgery clinic, we often encounter patients who are found to have lung nodules during physical examinations, and they ask nervously, "Is it lung cancer?" Lung nodules can be benign or malignant. Benign nodules include pulmonary tuberculoma, benign lung tumors (hamartoma, lipoma, etc.), lung inflammation (spherical pneumonia, inflammatory pseudotumor), lung cysts, pulmonary sequestration, etc.; malignant nodules include primary malignant tumors (lung cancer, carcinoid) and secondary malignant tumors (metastatic cancer). First, ask whether the patient has any recent discomfort symptoms, such as cough, sputum, hemoptysis, chest pain, difficulty breathing, fever, weight loss, hoarseness, etc. Secondly, review the medical history, especially whether there have been other types of malignant tumors. If you have had a chest X-ray or chest CT scan before, find it and compare it with the film of this examination to see whether the nodule is a recent occurrence or has existed before. Pathological diagnosis is the ultimate basis for determining the nature of pulmonary nodules. If the patient has sputum, the sputum can be examined for tumor cells and tuberculosis bacteria. If there is pleural effusion, the fluid can be extracted by puncture for cytological examination. Fiberoptic bronchoscopic biopsy is suitable for central lesions close to large airways, while CT-guided puncture is suitable for peripheral lesions close to the chest wall. Cytological examination and biopsy may give negative results for real tumor lesions due to the limitation of sample amount and sampling site. In this case, other methods can be used, such as blood tumor markers (SCC-squamous cell carcinoma, CEA-adenocarcinoma, NSE-small cell carcinoma), isotope tumor imaging, PET-CT, tuberculin skin test (PPD), erythrocyte sedimentation rate, blood tuberculosis antibodies, etc. to indirectly provide diagnostic reference opinions. A history of tumors in other parts of the body is important for the diagnosis of lung metastatic tumors. If the nature of the lesion still cannot be determined after the above examination process, two different treatment methods can be adopted according to the patient's wishes. The first is observation, with regular follow-up imaging examinations, initially at an interval of 3-6 months. If the lesion remains stable, it can be extended to 6-12 months for long-term observation. If the lesion shows a trend of enlargement during the observation process, surgical treatment should be adopted unless the patient's body cannot tolerate it. If inflammation is suspected, give 1-2 weeks of anti-infection treatment and then re-examine. It is suitable for patients whose physical conditions cannot tolerate surgery or who have fear and doubts about surgery. The second is surgical exploration, which uses thoracoscopy or small incision thoracotomy to locally remove the lesion and conduct a rapid pathological examination during the operation. If it is benign, the operation is ended. If it is malignant, the resection range is expanded and radical surgery is performed. It is suitable for patients who are physically able to tolerate surgery and are willing to undergo surgery. Before surgery, the patient needs to be evaluated in two aspects. First, cardiopulmonary function, to determine the patient's tolerance to surgery, Second, the clinical stage of the tumor, excluding possible distant metastases, patients with metastases are not suitable for radical surgery. |
Recommend
What medicine can cure hemorrhoids quickly?
Many urban white-collar workers have to sit at th...
What to do if there is no medicine for stomachache
Three meals a day are the normal food needs of th...
What is the treatment for autonomic nervous system disorders?
Speaking of autonomic nervous system disorder, ma...
Itchy throat, constant cough with mucus
An itchy throat, constant cough with mucus may be...
Treatment of finger bone hyperplasia
The disease of bone hyperplasia should not be unf...
What is the difference between laryngeal stridor and laryngeal wheezing?
Laryngeal gurgling and laryngeal stridor are both...
How to make beef jerky
Beef jerky is a delicacy that not many people are...
Definition of pernicious placenta previa
The reason why placenta previa is dangerous is th...
Are colds contagious? Why is it contagious?
In fact, cold is what we call the common cold in ...
Is Xiao Chaihu Decoction effective in treating colds?
Xiao Chaihu Decoction is relatively effective in ...
How to treat insufficient vitality
Insufficient vitality often leads to poor immunit...
What to do if you have a heat cold in summer?
In fact, heat cold is a kind of cold. If it is no...
Who is not suitable for chicken gizzard?
Chicken gizzard lining is not suitable for patien...
The incidence of not getting rabies vaccination
Rabies is a relatively serious disease, which is ...
How to check facial hyperactivity
As a parent, once you find that your child has an...